Robert Metcalfe and others developed the Ethernet protocol at Xerox PARC in 1973 as a wired communication protocol that links computers over a network. This is a widely used LAN protocol, also called Alto Aloha Network. A wide area network and an original area network are connected by it.
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet in computer networks refers to the most common type of Local Area Network (LAN) used at the moment. Due to its simplicity and the ability to support faster speeds with backward compatibility, it has grown along with technology advancements.
Why is Ethernet Used?
- Ethernet is still a common form of network connection, which is used for its high Speed, Security, and trustability.
- Ethernet can also be used to connect telephone lines and internet entry points to Wi-Fi routers and internet ports.
- Wireless connectivity may be used to link devices that are connected to the Internet, such as TVs, laptops, and other electronic gadgets.
- For different organizations, such as company headquarters, academy premises, and hospitals, actual networks are employed. Ethernet is popular because of its Speed, Security, and responsibility.
Types of Ethernet Networks
An Ethernet network generally is active in a 10 km fringe. Fiber optic cable extension significantly extends the distance covered by the network. Here are some types of Ethernet networks-
- Fast Ethernet- This type of Ethernet protocol is generally supported by a crooked cable or CAT5 cable, which has the implicit in transferring or admitting data at around 100 Mbps. They serve at 100Base and 10/100Base, on the fiber side of the link if any device similar to a camera, laptop, or other is connected to a network. The 100BASE- TX, 100BASE- FX, and 100BASE- T4 are the three orders of Fast Ethernet.
- Gigabit Ethernet- This type of network transfers data at an advanced speed of about 1000 Mbps or 1 Gbps. In this type of network, all the pairs in the crooked brace string contribute to the data transfer speed. This network type finds a large operation in video calling systems that use CAT5e or other advanced lines. In ultramodern times, gigabit Ethernet is more common.
- 10- Gigabit Ethernet- With a data transfer rate of 10 Gigabits per second, this is considered a much higher-speed and more advanced network. It makes use of CAT6a or CAT7 twisted-brace lines and optical fiber lines as well. With the aid of fiber optic cables, this network can be extended to almost any extent.
- Switch Ethernet- A switch or hub can be added to this type of network, which helps to increase its performance as each workstation in this network can have a separate 10Mbps connection instead of sharing the medium. For the rearmost Ethernet, it supports 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps and 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps for fast Ethernet.
Types of Ethernet Cables
In Ethernet cabling, there are three types of strings. These are –
Coaxial Cabling
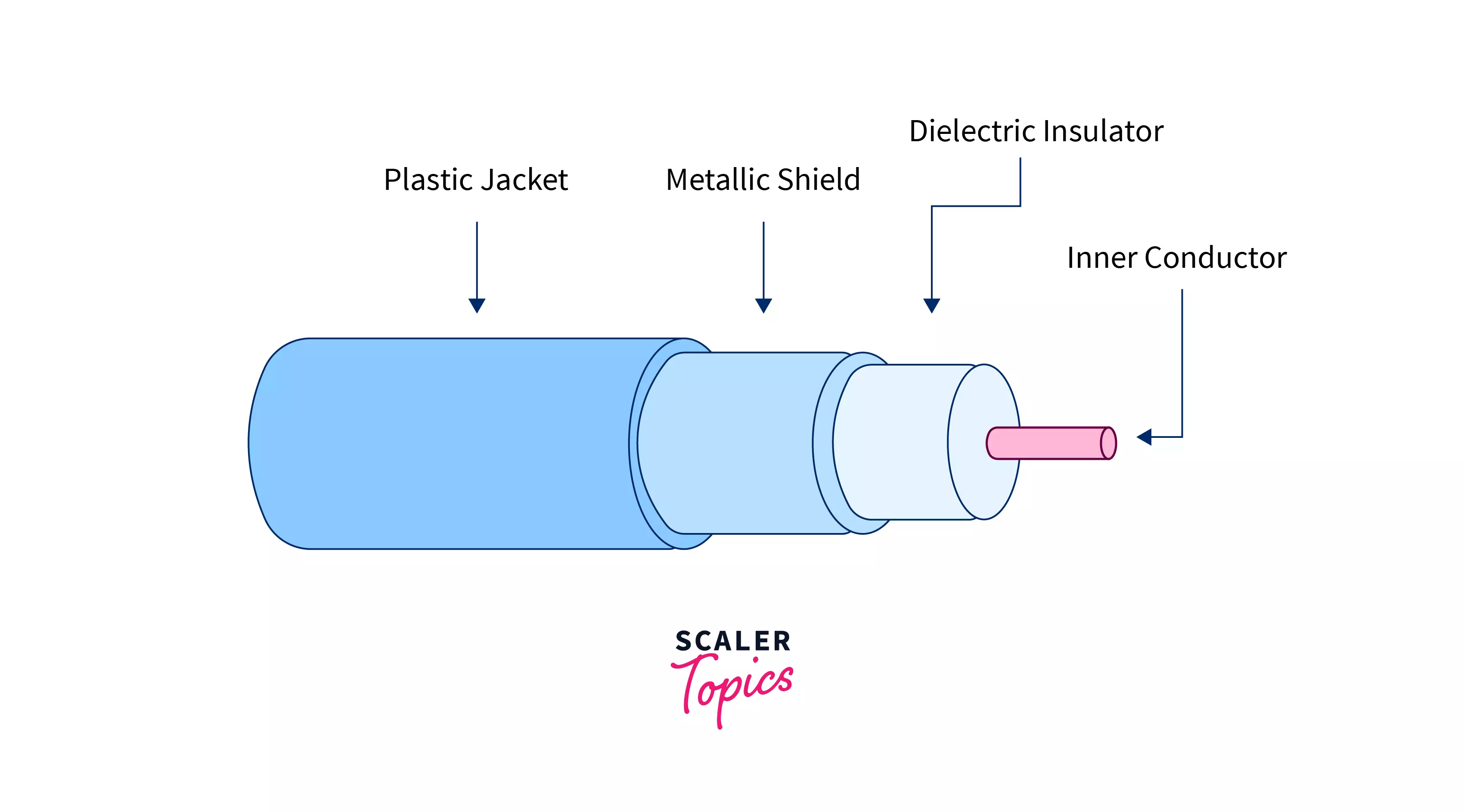
A coaxial cable has an inner conductor that runs down the middle of the cable. Conductors are encased in an insulation layer which is then encased by another conducting layer, making this type of cabling immune from outside interference. Coaxial cable was originally used in computer networks but is now largely replaced by crooked-brace cable. The common types of coaxial cable include:
- Hard line coaxial cable
- Flexible coaxial cable
- Semi-rigid coaxial cable
- Formable coaxial cable
- Rigid coaxial cable
- Twin axial cable
- Triaxial cable
Twisted-brace Cabling
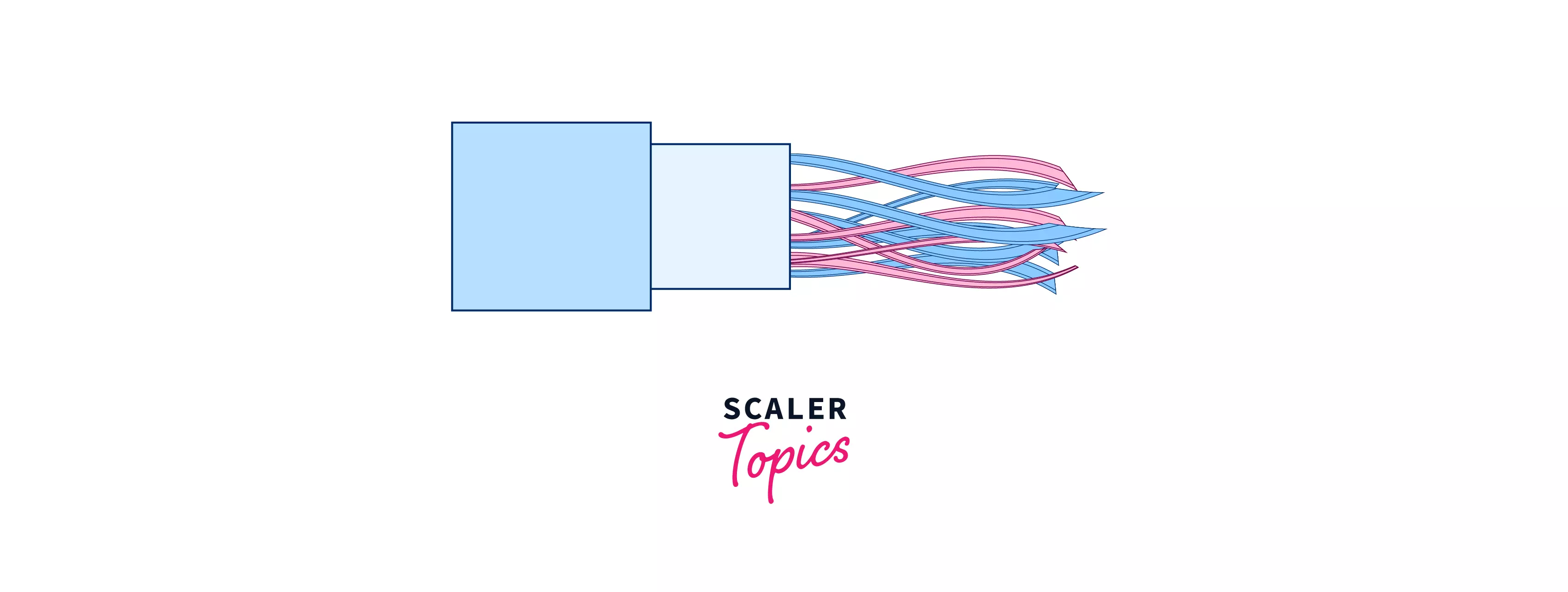
A Twisted-brace cable has four pairs of cables. These cables are twisted around each other to reduce crosstalk and outside hindrance. This type of cabling is common in current LANs. Twisted-brace cabling can be used for telephone and network cabling. It comes in two performances:
- UTP( Unshielded Twisted- Brace) Unshielded twisted pairs (UTPs) are enclosed by an outer jacket on a copper wire that has a resistance of 100 ohms. They do not possess a metal shield. The cable is left without electrical interference protection and has a tiny diameter. Its resistance to electrical noise and EMI is increased by the twist.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) STP has an additional copper braid jacket or foil wrapping to help insulate the cable signals from interference. STP cables are more expensive than UTP cables, but they have the advantage of supporting faster transmission rates over greater distances.
Fiber- Optical Cabling
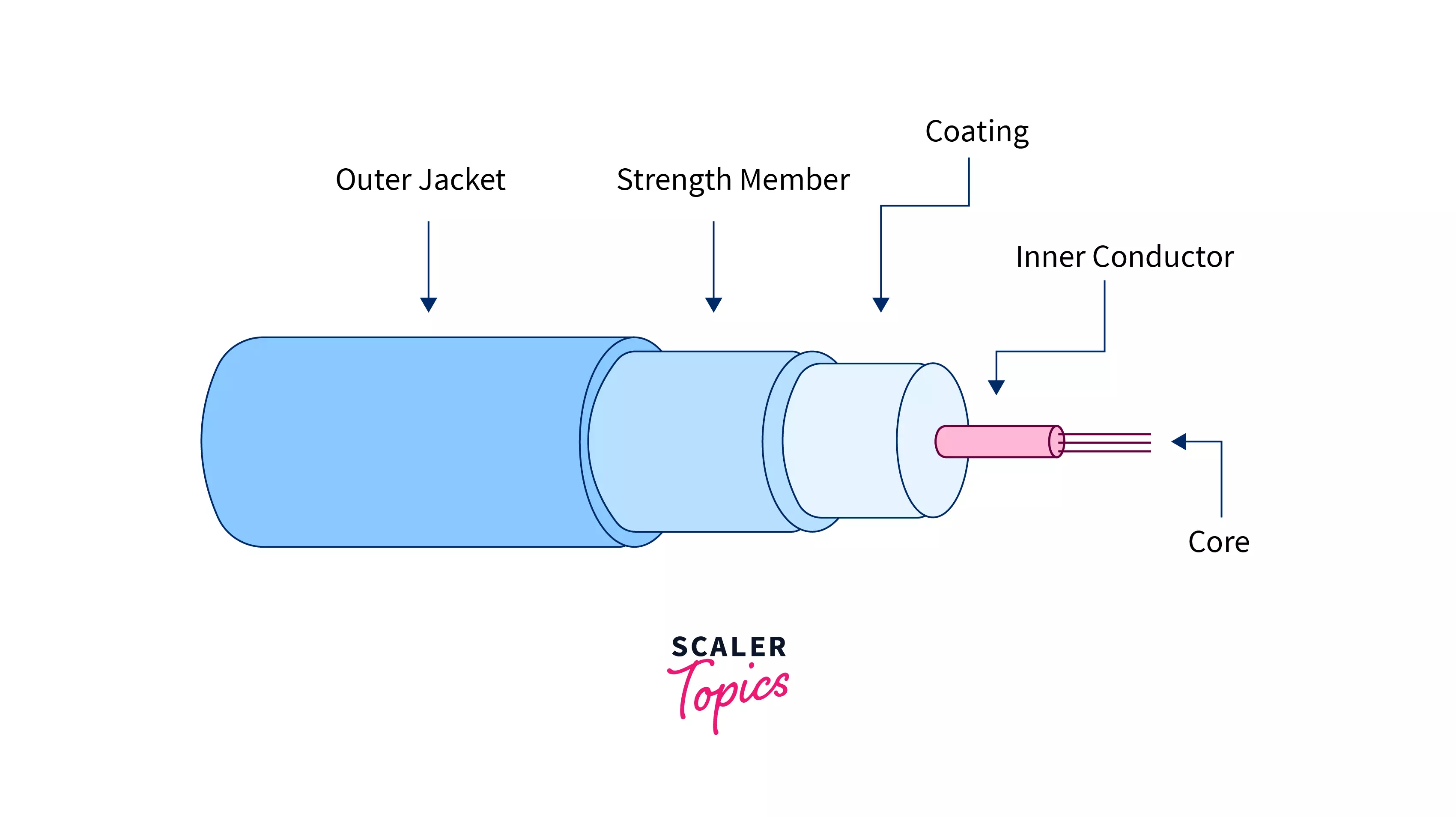 Structure
Structure
- Glass or acrylic are frequently used for the core and cladding. The index of refraction, which determines how fast light may go through a material and how much it will bend as it passes through it, is the most crucial basic characteristic. The core has a higher refractive index than the cladding. Due to reflection, it prevents light from escaping the fiber and entering the cladding.
- Strength members are designed to give the cable greater support, preventing optical fiber breaks. Strengthening members are positioned around the buffered optical strand in the tightly buffered cables.
- Cable may contain an additional layer of metallic shields for added physical protection. Since fiber is not exposed to EMI, it solely provides physical protection.
- The outer jacket is constructed of plastic, is available in a variety of colors, and must exceed fire-resistant standards.
- The coating acts as a barrier, shielding the core and cladding from breakage.
- The fiber cable’s buffer is a layer of protection that insulates the fiber from external stress. To ensure the strength of the cables, empty space in the tube is filled with protective material.
This type of cabling uses optic filaments to transmit data in the form of light signals. A cladding material surrounds the beaches of glass.
This type of cabling can support greater cable lengths than any other cabling type( up to a couple of long hauls). The lines are also secure from electromagnetic hindrances.
There are two types of Fiber-Optical Lines
- Single-mode fiber An optical fiber type frequently employed for transmission over greater distances is single-mode fiber. Only one transmission mode is present in single-mode fiber. It has greater bandwidth capabilities when compared to multi-mode fiber.
- Multi-mode fiber An optical fiber called a multi-mode fiber is made to transmit numerous light waves or modes simultaneously, each at a slightly varied internal reflection angle.
Advantages of Ethernet
- Speed: Speed offered by Ethernet is much more than the wireless connection. Due to Ethernet’s one-to-one connectivity, this is possible. As a result, a speed of 10 Gbps or occasionally 100 Gbps can be fluently achieved.
- Effectiveness: Ethernet cable like Cat6 consumes a lower quantum of power which is indeed lower than a Wi-Fi connection. So these types of ethernet lines are considered to be the most power-effective.
- Good data transfer quality: As it’s strong to noise, the quality of the information transferred does not degrade.
- Security: The Ethernet connection provides an advanced position of Security when compared to a wireless connection.
- Fairly low cost: To form an ethernet, we don’t need a higher cost. It’s affordable.
- Reliability: Ethernet connections are one of the most dependable connections because of their no or zero interruptions from the radio frequency. As a result, there’s a lower disposition, lower retardation, and no deficit of bandwidth.
Disadvantages of Ethernet
Indeed Ethernet has numerous advantages, but there are still some downsides to using an ethernet connection. These are the following disadvantages of Ethernet-
- Expandability: It is generally intended for shorter and lower distances. In case you want to expand the network, there will be fresh charges, and they are time-consuming in the Ethernet.
- The use of long lines can produce crosstalk.
- Connections: The number of connections is confined to Ethernet. If you’re using a single ethernet connection, only a single device can be connected if you want to connect multiple objects, you need to use further lines.
- Mobility: Mobility is limited. Ethernet is ideal to use in places where the device needs to sit in particular places.
- If there’s any problem with Ethernet, it’s delicate to troubleshoot. It is difficult to find which cable in the network is causing the trouble.
Conclusion
- Ethernet has been a widely used method of connecting computers. While its use may have been superseded by the Internet, most organizations still rely on Ethernet for their Security.
- Data has always been there in your gadgets in some or the other way; we can also say that it has always lived in your devices.
- Hence, we can say that the world that runs over Ethernet won’t be wrong.
- The users know the benefits they can get with Ethernet. Also, there have been considerable changes in this growing technology to meet the growing demand for data operations and connections.