Problem Statement
Given two sorted integer arrays of size m and n, Your task is to merge both the given sorted arrays into one so that the output array is also sorted.
The image below visualises the merge two sorted arrays problem.
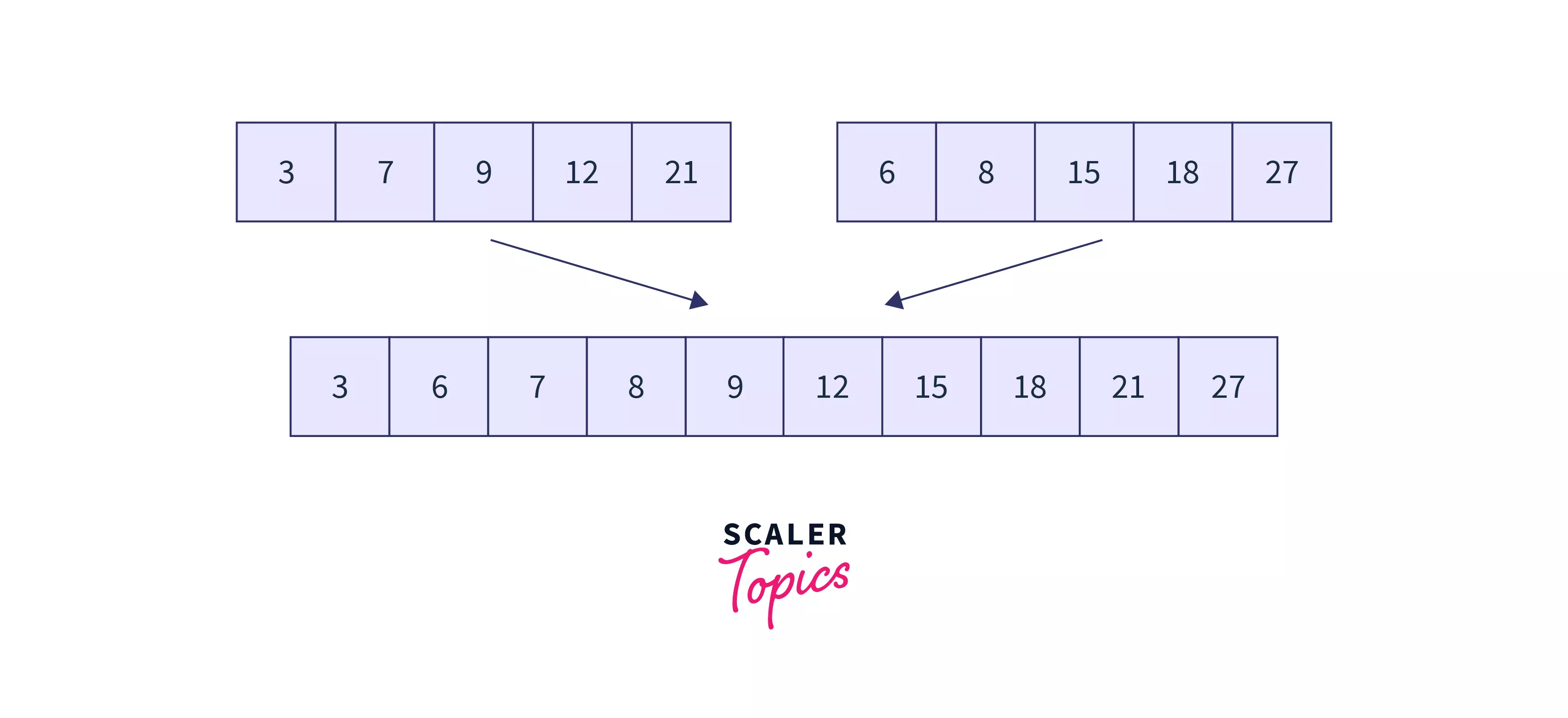
The constraints for the merge two sorted arrays problem are given below.
nums1.length == m
nums2.length == n
0 <= m, n <= 5000
1 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 100000
Example
Input:
m = 4 , n = 4
nums1[] = {1, 3, 4, 5}
nums2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8}
Output:
nums3[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8}
Approach-1: Naive Approach
In the naive approach, we insert all the elements from nums1[] and nums2[] into a new array nums3[] and, finally, sort it to get a sorted merge array.
Implementation (C++, Java, Python)
Let’s examine the code for the insertion sort approach in Java, Python, and C++.
C++ Implementation
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void mergeArrays(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n1, int n2, int arr3[])
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while(i < n1){
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
}
// now traverse arr2 and insert in arr3
while(j < n2){
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
// sort the whole array arr3
sort(arr3, arr3+n1+n2);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr1[] = {11, 15, 17};
int n1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int arr2[] = {2, 14, 26, 28, 39};
int n2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
int arr3[n1+n2];
mergeArrays(arr1, arr2, n1, n2, arr3);
for (int j=0; j < n1+n2; j++)
cout << arr3[j] << " ";
return 0;
}
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Java Implementation
// Java program to merge two sorted arrays
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeArrays {
public static void mergeArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int n1, int n2, int[] nums3) {
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// Traverse nums1 and insert its elements into nums3
while (i < n1) {
nums3[k++] = nums1[i++];
}
// Now traverse nums2 and insert its elements into nums3
while (j < n2) {
nums3[k++] = nums2[j++];
}
// Sort the whole array nums3
Arrays.sort(nums3);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums1 = {11, 15, 17};
int n1 = nums1.length;
int[] nums2 = {2, 14, 26, 28, 39};
int n2 = nums2.length;
int[] nums3 = new int[n1 + n2];
mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, n1, n2, nums3);
System.out.println("Array after merging");
for (int num : nums3)
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Python Implementation
def merge_arrays(nums1, nums2, n1, n2):
nums3 = nums1[:n1] + nums2[:n2]
nums3.sort()
return nums3
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
nums1 = [11, 15, 17]
nums2 = [2, 14, 26, 28, 39]
n1 = len(nums1)
n2 = len(nums2)
nums3 = merge_arrays(nums1, nums2, n1, n2)
print(*nums3)
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Complexity Analysis :
Time Complexity: O((m+n) log(m+n))
Space Complexity: O(m+n)
Approach – 2: Insertion Sort Approach
In the Insertion Sort approach of the merge two sorted arrays problem, we make an array nums3[] of size m+n and insert all the elements of input array nums1[] in the array nums3[] and then insert every element of nums2[] by applying insertion sort to get the sorted array as an output.
Algorithm:
- Create an array of size m+n named nums3[].
- Copy all elements of nums1[] to nums3[].
- Now traverse the elements of nums2[] and insert elements one by one to nums3[] by using the insertion sort.
Implementation (C++, Java, Python)
Let’s examine the code for the insertion sort approach in Java, Python, and C++.
C++ Implementation
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void merge(int nums1[], int nums2[], int m, int n) {
int nums3[m+n];
// copy nums1[] elements to nums3[]
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
nums3[i]=nums1[i];
//apply insertion sort algorithm to insert nums2[] element in nums3[]
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int temp=nums2[i];
int j=m-1;
for(;j>=0;j--){
if(nums3[j]>temp){
nums3[j+1]=nums3[j];
}
else
break;
}
m=m+1;
//put Current element at its correct position.
nums3[j+1]=temp;
}
// printing the resultant array
cout << "Array after merging" <<endl;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
cout<<nums3[i]<<" ";
}
int main(){
// The driver code
int nums1[] = {1, 3, 5, 7};
int nums2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int m = sizeof(nums1) / sizeof(nums1[0]);
int n = sizeof(nums2) / sizeof(nums2[0]);
// calling our function
merge(nums1, nums2, m, n);
return 0;
}
Output:
Array after merging
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Java Implementation
// Java program to merge two sorted arrays
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class MergeTwoSorted{
// function to merge arrays
public static void mergeArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int m,int n, int[] nums3){
// copy nums1[] elements to nums3[]
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
nums3[i]=nums1[i];
// apply insertion sort algorithm to insert nums2[] elements to nums1[]
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
int temp=nums2[i];
int j=m-1;
for(;j>=0;j--){
//move elements one position ahead that is greater than the current value
if(nums3[j]>temp){
nums3[j+1]=nums3[j];
}
else
break;
}
m=m+1;
//put Current element at its correct position.
nums3[j+1]=temp;
}
}
// driver code
public static void main (String[] args){
int[] nums1 = {11, 15, 17};
int m = nums1.length;
int[] nums2 = {2, 14, 26, 28, 39};
int n = nums2.length;
int[] nums3 = new int[m+n];
// calling function to merge two sorted arrays
mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, m, n, nums3);
// printing the resultant sorted array
for (int j=0; j < m+n; j++)
System.out.print(nums3[j] + " ");
}
}
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Python Implementation
# Python program to merge
# Two sorted arrays
# Merge nums1[0..m-1] and
# nums2[0..n-1] into
# nums3[0..m+n-1]
def mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, m, n):
#create an empty array for storing the result
nums3 = [None] * (m+n)
i = 0
j = 0
k = 0
#copy element of nums1[] to nums3[]
while i < m:
nums3[i]=nums1[i]
i=i+1
i=0
#Apply insertion sort algorithm to insert nums2[] elements into nums3[]
while i<n:
t=nums2[i]
j=m-1
while j>=0:
if nums3[j]>t:
nums3[j+1]=nums3[j]
else:
break
j=j-1
m=m+1
#put the Current element in its correct position.
nums3[j+1]=t
i=i+1
#print the resultant array
for i in nums3:
print(str(i), end = " ")
# Driver code
nums1 = [11, 15, 17]
m = len(nums1)
nums2= [2, 14, 26, 28, 39]
n = len(nums2)
#call function to merge sorted arrays
mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, m, n)
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Complexity Analysis :
Time Complexity: O(m∗n).
Space Complexity: O(m+n).
Approach – 3: Merge Sort
In the Merge Sort approach of the merge sorted arrays problem, we merge elements of two input sorted arrays using the merge sort algorithm. In merge sort, we traverse both input arrays simultaneously and apply a merge sort algorithm to get sorted resultant arrays.
Algorithm:
- Create an array nums3[] of size m+n to store the resultant sorted array.
- Start simultaneously traversing both input array nums1[] and nums2[].
- Choose a current smaller element from nums1[] and nums2[] and copy this element to nums3[] and increment the pointer of nums3[] and the array whose elements you have chosen.
- If there are elements left in nums1[] or nums2[], then copy all the left elements to nums3[].
Implementation (C++, Java, Python)
Let’s examine the code for the merge sort approach in Java, Python, and C++.
C++ Implementation
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Merge nums1[0..m-1] and nums2[0..n-1] into
// nums3[0..m+n-1]
void mergeArrays(int nums1[], int nums2[], int m,int n, int nums3[]){
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
// Traverse both array
while (i<m && j <n){
// Check if the current element of first
// array is smaller than the current element
// of the second array. If yes, store first
// array element and increment first array
// index. Otherwise, do the same with the second array
if (nums1[i] < nums2[j])
nums3[k++] = nums1[i++];
else
nums3[k++] = nums2[j++];
}
// Store remaining elements of the first array
while (i < m)
nums3[k++] = nums1[i++];
// Store remaining elements of the second array
while (j < n)
nums3[k++] = nums2[j++];
}
// Driver code
int main(){
int nums1[] = {11, 15, 17};
int m = sizeof(nums1) / sizeof(nums1[0]);
int nums2[] = {2, 14, 26, 28, 39};
int n = sizeof(nums2) / sizeof(nums2[0]);
int nums3[m+n];
mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, m, n, nums3);
for (int k=0; k < m+n; k++)
cout << nums3[k] << " ";
return 0;
}
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Java Implementation
// Java program to merge two sorted arrays
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class MergeTwoSorted{
// Merge nums1[0..m-1] and nums2[0..n-1]
// into nums3[0..m+n-1]
public static void mergeArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int m,int n, int[] nums3){
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// Traverse both array
while (i<m && j <n){
// Check if the current element of first
// array is smaller than the current element
// of the second array. If yes, store first
// array element and increment first array
// index. Otherwise, do the same with the second array
if (nums1[i] < nums2[j])
nums3[k++] = nums1[i++];
else
nums3[k++] = nums2[j++];
}
// Store remaining elements of the first array
while (i < m)
nums3[k++] = nums1[i++];
// Store remaining elements of the second array
while (j < n)
nums3[k++] = nums2[j++];
}
public static void main (String[] args){
int[] nums1 = {11, 15, 17};
int m = nums1.length;
int[] nums2 = {2, 14, 26, 28, 39};
int n = nums2.length;
int[] nums3 = new int[m+n];
mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, m, n, nums3);
for (int k=0; k < m+n; k++)
System.out.print(nums3[k] + " ");
}
}
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Python Implementation
# Python program to merge
# Two sorted arrays
# Merge nums1[0..m-1] and
# nums2[0..n-1] into
# nums3[0..m+n-1]
def mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, m, n):
nums3 = [None] * (m+n)
i = 0
j = 0
k = 0
# Traverse both arrays
while i < m and j < n:
# Check if the current element
# of the first array is smaller
# than a current element of
# second array. If yes,
# store first array element
# and increment the first array
# index. Otherwise, do the same
# With the second array
if nums1[i] < nums2[j]:
nums3[k] = nums1[i]
k = k + 1
i = i + 1
else:
nums3[k] = nums2[j]
k = k + 1
j = j + 1
# Store remaining elements
# of the first array
while i < m:
nums3[k] = nums1[i];
k = k + 1
i = i + 1
# Store remaining elements
# of the second array
while j < n:
nums3[k] = nums2[j];
k = k + 1
j = j + 1
for i in range(m+n):
print(str(nums3[i]), end = " ")
# Driver code
nums1 = [11, 15, 17]
m = len(nums1)
nums2 = [2, 14, 26, 28, 39]
n = len(nums2)
mergeArrays(nums1,nums2, m, n);
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(m+n).
Space Complexity: O(m+n).
To learn how to merge two sorted arrays without extra space, refer to Merge Two Sorted Arrays Without Extra Space.
Approach-4: Using Maps (O(mlog(m) + nlog(n)) Time and O(M+N) Extra Space
In this approach, we use a map to store the values of both the input array and the output array, and then we print the map’s keys to get sorted elements as an output.
Algorithm:
- Create an empty map.
- Traverse both input arrays individually and store the array element as a key in the map.
- Then, print the key set of the map.
Implementation (C++, Java, Python)
Let us see code in C++, Java, Python
C++ Implementation
// C++ program to merge two sorted arrays
//using maps
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to merge arrays
void mergeArrays(int nums1[], int nums2[], int m, int n){
// Declaring a map.
// using map as an inbuilt tool
// to store elements in sorted order.
map<int, bool> mp;
// Inserting values to a map.
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
mp[nums1[i]] = true;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
mp[nums2[i]] = true;
// Printing keys of the map.
for(auto i: mp)
cout<< i.first <<" ";
}
// Driver Code
int main(){
int nums1[] = {11, 15, 17}, nums2[] = {2, 14, 26, 28, 39};
int size = sizeof(nums1)/sizeof(int);
int size1 = sizeof(nums2)/sizeof(int);
// Function call
mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, size, size1);
return 0;
}
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Java Implementation
// Java program to merge two sorted arrays
//using maps
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class MergeTwoSorted {
// Function to merge arrays
static void mergeArrays(int nums1[], int nums2[], int m, int n){
// Declaring a map.
// using map as an inbuilt tool
// to store elements in sorted order.
Map<Integer,Boolean> h1 = new TreeMap<Integer,Boolean>();
// Inserting values to a map.
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
h1.put(nums1[i], true);
}
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
h1.put(nums2[i], true);
}
// Printing keys of the map.
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Boolean> me : h1.entrySet()){
System.out.print(me.getKey() + " ");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args){
int nums1[] = {11, 15, 17}, nums2[] = {2, 14, 26, 28, 39};
int size = nums1.length;
int size1 = nums2.length;
// Function call
mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, size, size1);
}
}
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Python Implementation
# Python program to merge two sorted arrays
# using maps
import bisect
# Function to merge arrays
def mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, m, n):
# Declaring a map.
# using the map as an inbuilt tool
# to store elements in sorted order.
mp=[]
# Inserting values to a map.
for i in range(m):
bisect.insort(mp, nums1[i])
for i in range(n):
bisect.insort(mp, nums2[i])
# Printing keys of the map.
for i in mp:
print(i,end=' ')
# Driver code
nums1 = [11, 15, 17]
nums2 = [2, 14, 26, 28, 39]
size = len(nums1)
size1 = len(nums2)
# Function call
mergeArrays(nums1, nums2, size, size1)
Output:
2 11 14 15 17 26 28 39
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: The time complexity of this approach is O(mlogm+nlogn).
Space Complexity: O(m+n)
Explore Scaler Topics Data Structures Tutorial and enhance your DSA skills with Reading Tracks and Challenges.
Conclusion
In the merge sorted array problem, we are given two input sorted arrays and have to return the merged sorted array of both input arrays.
- The merge sorted array problem can be solved using three approaches.
- Insertion sort approach solution of this problem solves this in O(m∗n)O(m∗n) time complexity .
- Merge sort approach takes O(m+n)O(m+n) time to solve this problem.
- We can also solve this problem using a map which gives us O(mlogm+nlogn)O(mlogm+nlogn) time complexity .