Cryptography is a term used in data communication that refers to protecting the private information shared between two parties. Network Security refers to securing and protecting the network and data to ensure the confidentiality of data.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography generally deals with the study and practice of techniques for ensuring secure communication between two parties in the presence of a third party called adversaries.
Below image to visualize the encryption process

Let us understand cryptography with the help of an example. As we see in the above figure sender wants to send a “hello” message and encryption is done on the sender to convert the sender’s message into an unreadable format (cipher text) using the encryption key.
The message of the sender also known as plain text is converted into an unreadable form by using a key ‘k’, that unreadable resultant text is called cipher text. And this whole process is known as encryption.
At the receiver side cipher text is received and that cipher text is again converted into plain text using the decryption key.
Decryption is the reverse process of encryption. In decryption, at the receiver end cipher text is converted into plain text using the key, so the receiver can understand it.
Now let us understand the terms secure communication and adversary one by one.
- Secure Communication generally refers to rules and regulations that ensure that the data shared between two communicating parties can not be retrieved by the adversary.
- In cryptography, an adversary refers to a malicious entity, whose target is to access data by threatening the protocols of cyber security.
- Cryptography deals with the creation and analysis of rules to prevent the third party from retrieving private information shared between two parties.
The Main principles of cryptography are Confidentiality, Data Integrity, Authentication, Non-repudiation
- Confidentiality refers to rules and regulations that make sure that the data is restricted to certain people or certain places.
- Data integrity ensures that data remains accurate and consistent over its whole transmission process.
- Authentication ensures that the data is being claimed by the person who is related to it.
- Non-repudiation ensures that a person or a party related to the transmission process cannot deny the authenticity of their signature on the data or the transmission of a message.
What is Network Security?
Network Security generally refers to action taken by an enterprise or organization to protect and secure its computer network and data. The main aim is to ensure the confidentiality and accessibility of the network and data.
Below image to show the network security model:
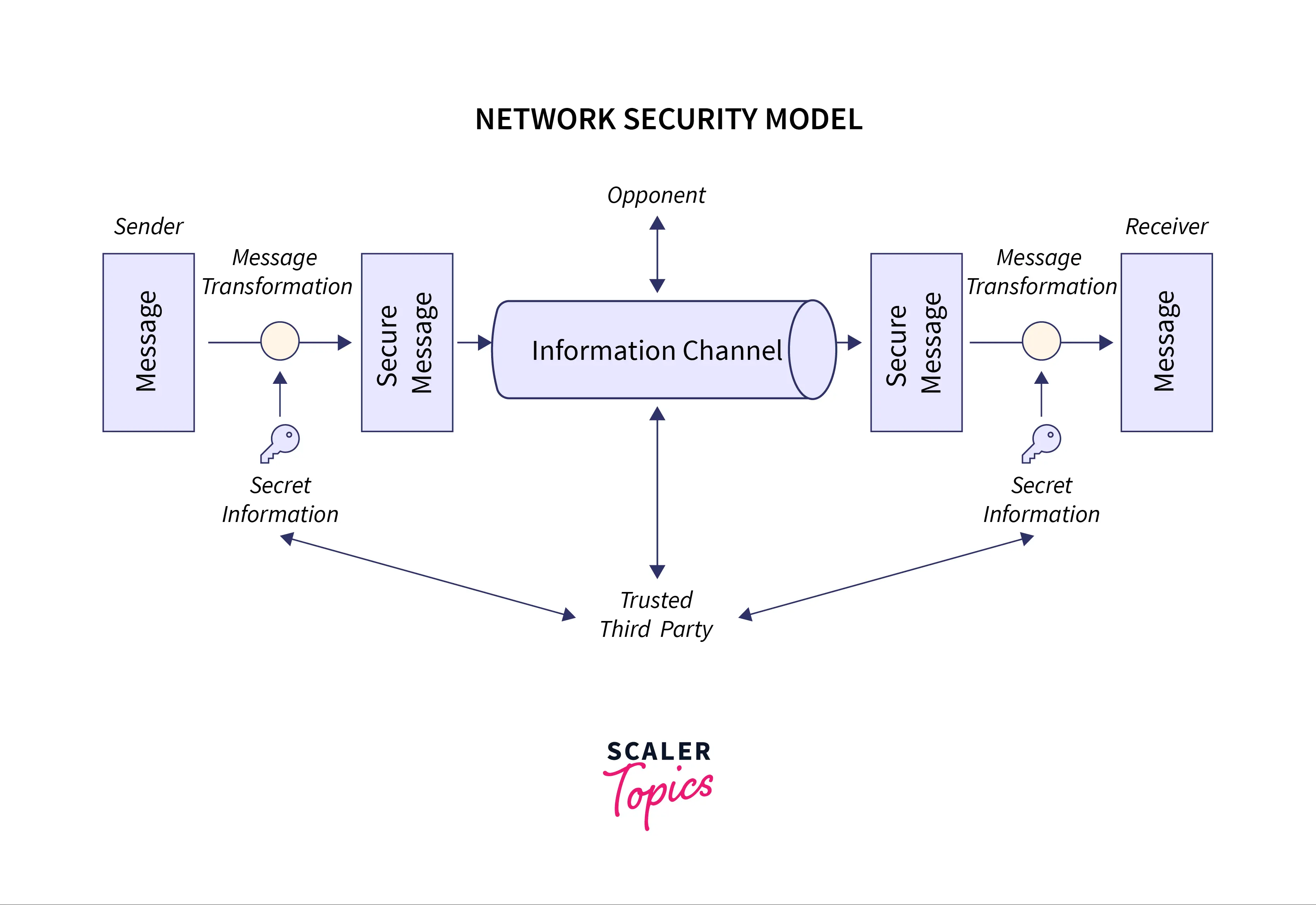
The network security model represents the secure communication between sender and receiver. This model depicts how the security service has been implemented over the network to prevent the opponent from causing a threat to the authenticity or confidentiality of the data that is being communicated through the network.
- Network security covers a huge amount of technologies, devices, and processes
- In simple words, it is a set of rules and regulations designed for protecting and securing the integrity, confidentiality, and accessibility of data and computer networks.
- The most common example of network security is password protection which was chosen by itself.
Importance of Cryptography and Network Security
Importance of Cryptography
Cryptography is very important for protecting private information from third-party access. Some of the importance of cryptography are given below:
- For secure communication, data transmission, and transactions.
- To safeguard personal information
- To ensure data confidentiality
- For the protection of data from unauthorized access.
- To authenticate the source of data
- To establish trust between two communicating parties.
Cryptography provides above all features by converting the sender message into an unreadable format while transmitting over the network so that it can not be accessed by any unauthorized user.
Importance of Network Security
- To protect sensitive information safe from cyber-attacks.
- This is important to secure sensitive data safe from cyber attacks and to ensure that the network is usable and can be trusted
- Network security protects the data of the client by ensuring that hackers can not get into your network easily.
- Network security also improves the performance of the network by ensuring that the system is not slowed down due to redundant tools and data.
- To protect the network from a ransomware attack. Ransomware is a common type of attack that blocks access to your data until you pay the ransom.
Applications of Cryptography and Network Security
Cryptography Applications
- Authentication/Digital Signatures
- Time Stamping
- Electronic Money
- Encryption/Decryption in email
- WhatsApp Encryption
- Instagram Encryption
- Sim card Authentication
Network Security Applications
- Protection of network.
- Protection from intrusions.
- To protect from threats.
- Protection of data from breaches
Become a networking enthusiast with our Free Computer Networking course. Join now and learn to create, troubleshoot, & optimize computer networks.
Conclusion
- Cryptography and network security are two of the networking terms used for the protection and security of data and networks.
- Cryptography is used to protect the private information shared between two communicating parties from a third party.
- Confidentiality, Data Integrity, Authentication, and Non-Repudiation are the main principles of cryptography.
- Network security is the actions taken or procedures followed to protect the computer network.
- Cryptography ensures data confidentiality and provides data protection from unauthorized access.
- Network security protects the sensitive data of clients and it protects the network from ransomware.